


Did you know that some people are earning six-figures from the comfort of their own homes by tapping into the world of online jobs? It's true, and it’s reshaping the way we think about work.
With remote work skyrocketing due to recent global events, more people than ever are exploring digital opportunities. Understanding online job dynamics is crucial in today’s economy.

Surprisingly, the most successful online professionals aren’t necessarily those with the fanciest resumes. Instead, they're leveraging niche skills and unconventional strategies. Consider the rise of TikTok marketing experts who are earning big. These savvy digital nomads have understood how to harness the power of social platforms to create new income streams. But that’s not even the wildest part…
Contrary to popular belief, the highest demand isn't just in tech fields. Creative roles, such as virtual reality experiences and sustainable design, are booming. This shift is democratizing access to high-paying online jobs, highlighting the need for a diverse skill set. But the real shocker is the unexpected backgrounds of these online job pioneers…
What happens next shocked even the experts: People from all walks of life are discovering untapped potential and dramatically changing their lifestyles. So, how exactly are they doing it? Stay tuned as we explore the most surprising trends and techniques in the online job market that you need to know!
In the midst of the digital revolution, creative freelancing has emerged as a powerhouse. No longer confined to traditional art studios, artists are achieving global reach with platforms like Etsy. Many are surprised to learn that unconventional art forms, from recycled art to digital animations, are not only gaining popularity but also commanding premium prices. But there’s one more twist to this creative surge…

Freelancers with skills in graphic design, video production, and custom illustration are experiencing unprecedented success. The demand for personalized and tailored digital content is soaring. These creators are not just earning a wage but crafting resonant brand stories that captivate audiences worldwide. Still, what's driving this voracious appetite for creativity?
The shift towards remote work has made companies more reliant on creative freelancers to keep content fresh and engaging. This trend is fueling an increase in jobs that require out-of-the-box thinking and a knack for capturing trends before they take off. As the competition intensifies, freelancers are finding new, lucrative niches that are set to shape the future of work. What you read next might change how you see this forever.
Understanding the creative freelancing landscape involves more than just knowing where to find work. It requires innovation and adaptability, with freelancers setting trends rather than merely following them. The interconnectedness of the digital world makes it necessary to constantly reinvent oneself to stay ahead. But the real game-changer is how ordinary people are leveraging these trends to their advantage...
The rise of micro-tasks offers a fascinating glimpse into the future of online work. Platforms like Amazon's Mechanical Turk have transformed it into a thriving ecosystem where small jobs translate into substantial income over time. It's a hidden gem for those who prefer flexibility and diversity in their work routine. Why has this market remained largely untapped until now?

Micro-task platforms appeal to a broad range of participants, from students to retirees, proving that anyone can dive into this form of online work with minimal barriers to entry. Interestingly, the earning potential grows as individuals become more adept at picking high-value tasks, turning seemingly insignificant gigs into profitable ventures. But the full potential of micro-tasks goes even further…
Companies are increasingly outsourcing micro-tasks to manage workloads more efficiently while still achieving high-quality results. This strategic outsourcing is driving demand in data entry, content moderation, and even simple coding tasks. Recognizing which micro-tasks offer the best returns is pivotal for maximizing success. What insightful trends are emerging from this growing sector?
The allure of micro-tasks goes beyond just the monetary benefits; it introduces a new form of professional freedom. Participants can tailor their work to fit their lifestyle, choosing tasks that align with their interests. The fragmenting of traditional job roles into smaller, actionable tasks is revolutionizing job satisfaction and flexibility. And just when you think it couldn't get any more appealing…
As fitness studios closed their doors, the online fitness industry surged forward dynamically. Trainers have shifted from in-person sessions to virtual platforms, discovering global clientele eager for personalized exercise regimes. It's not just about workouts; it's an immersive lifestyle transformation that's attracting millions. But the story gets even more fascinating…
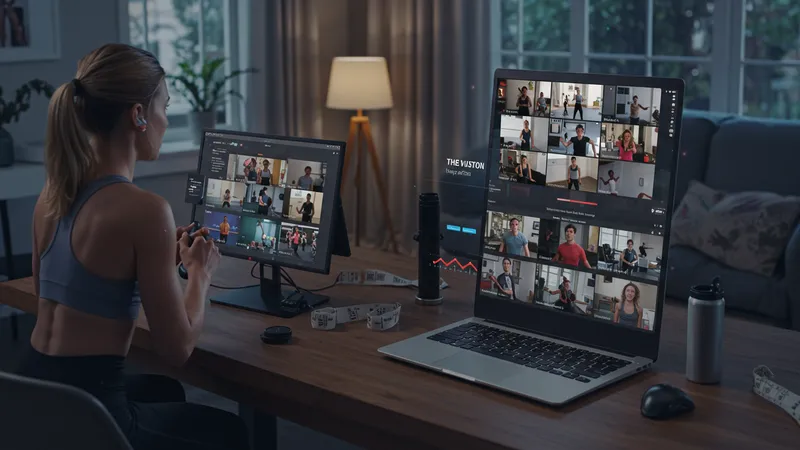
Innovative apps like Peloton and Zwift have turned fitness into engaging, community-driven experiences. By leveraging real-time interaction and competition, they have redefined exercise as a social and rewarding pursuit. These platforms have made it feasible for trainers to monetize their expertise without geographical restrictions. What's the secret ingredient in their explosive growth?
The advent of portable technology and health-tracking devices has amplified opportunities for remote fitness jobs. Trainers can now offer more personalized advice and guidance based on clients’ data, enhancing customer engagement and retention. This trend suggests a promising future for fitness professionals ready to adapt. Yet, there’s an unexpected tech twist fueling this shift…
This digital pivot signifies more than just convenience; it's a paradigm shift to holistic health cultures that prioritize long-term wellness. As trainers curate holistic packages encompassing diet, mental health, and physical fitness, they are tapping into an increasing market demand. But the greater surprise lies in how this realignment is empowering everyday enthusiasts…
Virtual reality (VR) is transcending the gaming world, offering groundbreaking opportunities in sectors like education and tourism. Companies are now using VR to provide richer, immersive experiences, giving users a taste of possibilities beyond the confines of a gaming console. What's allowing VR to escape the confines of traditional gaming?
Industries such as real estate and healthcare are adopting VR technologies for training and customer engagement, highlighting its adaptability and potential for profit. By simulating real-world scenarios, they provide an efficient, cost-effective, and risk-free method of learning and evaluation. However, what does this signify for everyday online job seekers?
The demand for VR content creation is on the rise, prompting companies to hire developers, designers, and storytellers who can innovate within this burgeoning field. New job roles are emerging, drawing those eager to engage viewers through captivating and interactive content. The financial incentives are promising, but how quickly can one capitalize on these trends?
Despite being initially pigeonholed, VR is becoming integral to various professional landscapes. For online job seekers, embracing this technology offers a unique advantage, opening avenues yet unexplored by many. As VR becomes more mainstream, are we witnessing the dawn of a new digital frontier that will redefine job markets? Prepare to uncover even more staggering insights…
The rise of eco-conscious online jobs is a reflection of society’s commitment to sustainability. With green living becoming a priority, digital roles in environmental advocacy and sustainable development are gaining traction. It's not just a trend; it's a vital shift towards preserving our planet. Does this signal a transformative era for online employment?

Online roles in eco-friendly product development and carbon footprint management are opening up, offering creative ways for individuals to contribute to environmental causes. By working remotely with organizations committed to green initiatives, people can align their professional goals with their personal values. But how are companies fostering this new digital ecosystem?
Incorporating sustainability practices into business models has become a competitive advantage, drawing more consumers and investors. This evolution is generating a rich variety of jobs that prioritize eco-friendly methodologies, inviting fresh and innovative perspectives. What are the broader implications of this movement on the future workforce?
These rapidly evolving roles are not only about combating climate change but also about integrating sustainability into everyday business operations. The scope for innovation in sustainable tech means an ever-expanding selection of jobs for the environmentally conscious professional. What makes these positions uniquely fulfilling? Discover the full potential that awaits life on this green frontier…
The cryptocurrency market has spawned a plethora of new job opportunities, offering more than just investment potential. As interest in decentralized finance grows, roles focused on blockchain technology, crypto consultancy, and compliance are becoming increasingly lucrative. Has cryptocurrency truly crossed into the mainstream job market?
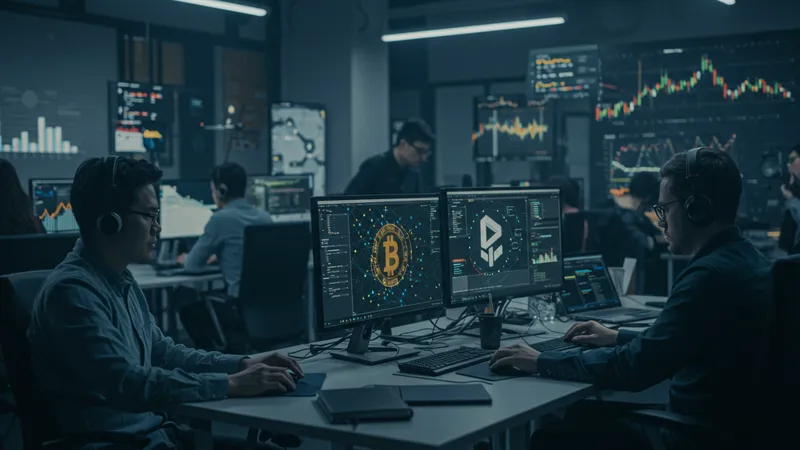

Demand for blockchain developers and crypto marketing specialists reflects a broader acceptance and integration of digital currencies. Businesses keen to harness crypto advantages are scouting proficient talent capable of navigating the nuanced world of digital finance. What unique skills do candidates need to excel here?
For many, the allure of cryptocurrency careers lies in their potential for high growth and dynamic work environments. As blockchain technology continues to disrupt traditional finance systems, new roles entrenched in creativity and technical expertise are being birthed. This might redefine the future of online financial employment. Does this growing ecosystem hold the key to unparalleled job security?
The merging of cryptocurrency with everyday online transactions is altering the employment landscape considerably. Its transparency, efficiency, and transformative capacity make it a formidable force for change. What's next for those diving into this uncharted territory? Brace yourself for more revelations that could redefine careers as we know them…
As the demand for online learning experiences expands, teaching from home has undergone a renaissance. Platforms like Coursera and MasterClass allow educators to reach global students without ever leaving their study. It appears online education is set to revolutionize the sector. But are we truly prepared for this paradigm shift?

The pandemic accelerated the adoption of e-learning, leading to burgeoning opportunities for educators specializing in niche subjects from astrophysics to music production. Flexibility and accessibility are key advantages, with the ability to cater to diverse learning styles. However, is accessibility sufficient to sustain this educational evolution?
Monetizing expertise extends beyond traditional curricula, with creators designing courses across a spectrum of interests. From personal development to creative arts, this democratization of knowledge empowers educators and learners alike. Yet, what ensures the credibility and efficacy of these digital classrooms?
Emerging technology and innovative teaching methodologies are transforming online education, pushing the boundaries of conventional learning. For educators embracing digital transformation, this shift promises unprecedented flexibility and global reach. What does this entail for the future learning landscape? Prepare for revelations that could reshape educational paths forever…
As our lives dive deeper into the digital realm, cybersecurity professions are becoming indispensable. The incidence of cyber threats is escalating, necessitating skilled individuals who can safeguard sensitive data. The demand for cybersecurity expertise is outpacing supply. Is this where exceptional career opportunities lie?

Cybersecurity roles like ethical hacking and data protection analysis are not only well-paying but critical to maintaining digital trust. Companies are willing to pay a premium for experts capable of predicting vulnerabilities. But have we fully grasped the scope of these roles and the threats they combat?
Significant investment is being channeled into cybersecurity, fostering a robust job market for IT professionals. Training programs are proliferating, designed to equip new entrants with specialized skills required by the industry. Yet, with cyber threats evolving, how can we keep pace with technological advancements?
The dynamic field of cybersecurity offers a wealth of opportunities, challenging professionals to stay ahead of malicious actors. For those choosing to delve into this sector, the rewards are both personal and financial. As companies digitize, how will this influence future efforts to guard digital infrastructures? Explore further for transformative insights…
The gig economy, fueled by platforms like Uber and TaskRabbit, represents a seismic shift in how work is approached today. This alternative model offers unparalleled freedom but also raises questions about sustainability and equity. Are we seeing a fleeting trend or a lasting transformation in the workforce?

While flexibility remains the gig economy's selling point, the lack of traditional employment benefits prompts an ongoing debate. Nevertheless, this new model allows workers to pursue personal passion projects simultaneously, representing a significant cultural shift. What's driving more individuals to embrace this unstructured work style?
As businesses adapt, there is an increasing endorsement of short-term contracts over permanent hires. This preference has broadened the scope of the gig economy, making it appealing to professionals seeking variety and autonomy. But will this unconventional approach continue to thrive amid growing regulatory scrutiny?
The rise of gig work introduces complex challenges concerning fairness, stability, and regulation. As it matures, the gig economy presents a transformative potential to redefine both employers’ and workers' expectations. What lies ahead for this expanding sector? Stay tuned for insights into its projected trajectory…
AI and automation are not only reshaping existing roles but creating new ones, ushering in an era of unprecedented job evolution. From AI ethicists to automation testers, new fields are blossoming. The future job market is poised for dynamic change, but how do we prepare for it today?

With AI systems becoming more integrated into various industries, demand for skills related to machine learning and robotics is skyrocketing. As automation takes over routine tasks, professionals can focus more on complex problem-solving and innovation. But how does one stand out in an increasingly competitive landscape?
The rise of AI technologies requires a shift from traditional education paradigms to more specialized training programs. Upskilling in AI-related technologies is becoming a necessity for tech professionals aiming to unleash career advancements. But with automation growing rapidly, what opportunities will remain untouched by machines?
Amidst technological disruptions, understanding and leveraging AI are key to carving out successful careers. For industries undergoing transformation, this means embracing new roles tailored to a future dominated by smart technologies. How will AI further redefine job markets? Expect astonishing revelations to emerge as this narrative continues…
The demand for remote customer service roles has surged, mirroring the shift towards digital interaction. Companies are not only looking for tech-savvy individuals but also those with excellent communication skills. What factors are driving this surge in remote customer service positions?

Driven by a seamless user experience requirement, enterprises are investing in sophisticated communication channels. This investment has magnified the necessity for adept remote agents capable of resolving issues with ease. But what innovations are redefining customer service standards?
While technology enables remote solutions, the human touch remains indispensable in providing exceptional service. Companies are emphasizing empathy and adaptability, offering extensive training to refine these qualities among their support teams. But how do these roles compare with conventional positions in terms of career advancement?
Remote work in customer service offers flexibility, career growth, and the potential for a diversified skill set. As digital transformation continues, understanding the balance between human and technological interaction becomes critical for future success. How will this sector continue to evolve? Follow along for more…
Content creation has emerged as a vibrant frontier in the online job landscape. Whether it's through writing, podcasting, or video production, creators have found unprecedented opportunities to share their voices. What is fueling this creative diversity in the digital age?

Digital platforms have democratized content creation, enabling a broader spectrum of creative expression. Niche content, tailored to specific communities, reflects evolving consumer interests. But how do creators monetize their passion projects amidst this crowded field?
Cross-platform publishing opportunities are allowing creators to expand their reach and income through ad revenue, sponsorships, and merchandise. The evolving landscape demands constant adaptation to changing algorithms and audience preferences. What crucial strategies ensure sustained creative engagement?
As content continues to proliferate, creators who leverage analytics effectively can align their endeavors with audience demand. The ability to iterate quickly based on viewer feedback will determine long-term success. Are we witnessing the dawn of a new era for independent creators? Continue your exploration for answers…
Telemedicine is altering the landscape of healthcare jobs, with professionals now able to consult from anywhere. As telehealth services gain traction, healthcare workers enjoy more flexible work arrangements. What implications does this shift have on traditional healthcare models?
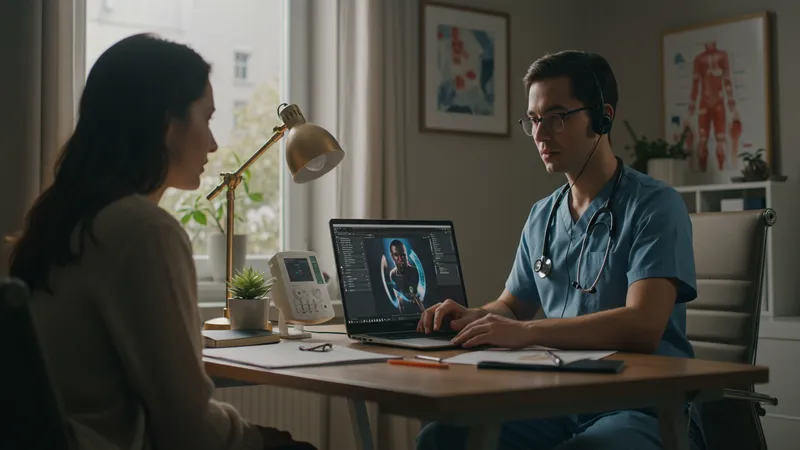

Access to healthcare services is expanding, bridging geographical barriers for clinicians and patients alike. The convenience and efficiency of virtual consultations have accelerated this shift, offering holistic benefits for both parties. Yet, how will it impact healthcare quality overall?
Embracing virtual consultations involves grappling with technological and regulatory challenges. As digital expectations heighten, healthcare professionals must ensure that services are not just efficient but also empathetic. Where does telemedicine stand in relation to patient satisfaction?
Blurring the line between traditional and digital care, telemedicine is reshaping healthcare delivery. Keeping pace with innovation ensures that professionals can harness new tools to enhance patient care. How long can traditional practices compete if they don’t evolve accordingly? Unveil the insights ahead…
The e-commerce boom is revolutionizing retail, with online platforms drawing consumers away from conventional shopping. Businesses are keen to capitalize on this digital wave to enhance their market reach. What differentiates innovative from stagnating e-commerce strategies?

The adoption of technology like AI in customer analytics and personalized recommendations represents a new era in shopping convenience. Retailers embracing advanced data strategies are capturing a larger slice of consumer engagement. How will emerging technologies redefine retail competition?
Savvy businesses are distributing products across multiple digital marketplaces, extending beyond traditional e-commerce giants. Understanding consumer purchasing behavior, they are adeptly positioning themselves for success. But what other tactics will bolster their longevity in the digital marketplace?
Redefining retail operations to match the digital consumer landscape involves astute strategy and forward-thinking innovation. Businesses able to adapt quickly are more likely to thrive as competition intensifies. Is this the ultimate test for retail survival? Find out what future maneuvers await…
In this age of digital revolution, online jobs offer a mosaic of opportunities for those willing to adapt and innovate. The spectrum of remote work reaches across industries, from creative niches to high-tech sectors, reshaping how we perceive conventional employment. The lesson here is profound: the future belongs to those bold enough to explore uncharted digital territories. So, reflect on these insights, share them with someone ready to embark on their own unique journey, and together, let's redefine what work means in the modern age.