


What if I told you there's a seismic shift unfolding that could redefine the landscape of not just one, but three major industries? Revolutionizing healthcare, real estate, and manufacturing isn't just a distant possibility—it's happening right now, and it's changing lives by the day.
In an era where technology is advancing at a pace faster than most can keep up, these industries are leveraging cutting-edge innovations that promise not just efficiency, but revolutionary change. If you think your sector is safe from this wave, think again.

Let's start with healthcare. Today, AI isn't just a tool; it's a partner in diagnosis and treatment. Take IBM Watson, which can analyze millions of clinical records and suggest personalized treatment plans with startling accuracy. But that’s not even the wildest part…
In real estate, virtual reality isn't just for gamers—agents are using it to offer potential buyers immersive property tours from their living rooms! This isn’t science fiction; it’s today’s reality. But that’s not even the wildest part…
The fusion of technology with traditional industries isn’t just enhancing possibilities; it's uprooting old methods and paving the way for unprecedented growth. But what's next could redefine everything we take for granted in these sectors, and experts are already preparing for a new era. What happens next shocked even the experts…
In the past decade, artificial intelligence has leapt from an experimental phase in healthcare to becoming an indispensable tool used in hospitals worldwide. Machines that learn can now suggest treatment plans for obscure diseases that not even experienced doctors can easily diagnose. AI algorithms by companies like Google's DeepMind are helping doctors predict patient deterioration earlier and with more precision, saving lives by nipping crises in the bud.

It's not just diagnoses that are being revolutionized. Personalized medicine is also seeing rapid advancements. Tailored treatments based on individual genetic profiles are becoming mainstream, thanks to AI-powered genomic analytics that reduce time and cost significantly. But there’s one more twist: The ethical implications of AI in healthcare raise complex questions needing urgent answers, challenging the boundaries of patient privacy and consent.
Telemedicine is another facet undergoing dramatic change. Tools like Doctor on Demand and Teladoc allow patients to consult physicians via video chat, bringing medical expertise into homes. The convenience factor is substantial, with reports indicating a decrease in unnecessary emergency room visits by up to 30%. But the rapid pace of adoption is also shining a spotlight on cybersecurity vulnerabilities that could endanger sensitive patient data.
As these technologies evolve, they stimulate a dialogue on the subtle balance between innovation and ethics. With healthcare experience now custom-fitted to individual needs through technology, the debate swirls: How much should we rely on machines for our most critical health decisions? The answer lies just around the corner, and what you read next might change how you see this forever.
The real estate sector is undergoing a technological makeover like never before. Virtual and augmented reality have moved beyond the realm of entertainment and into the world of property sales. Real estate agents now offer potential buyers the opportunity to step inside properties miles away without ever leaving their homes. Transactions that used to take months of planning and travel can now be streamlined into days, saving time and resources.

Imagine visiting dozens of apartments in a bustling city with no need for appointments or travel. This technology doesn't just benefit the buyer; sellers and agents are tapping into a global client base previously out of reach. Market giants like Matterport are leading the charge, boasting over two million VR spaces crafted across multiple continents.
The technology's capabilities extend beyond mere visuals. AI-driven analytics provide realtors with predictive insights into buyer behavior and market trends that were once impossible to decipher. By understanding precise buyer preferences and financial profiles, transactions are becoming increasingly personalized. But there's one more twist: These developments are prompting conversations around digital inclusivity and ensuring that tech is accessible to all players in the market.
Despite the advantages, this digital revolution poses challenges as well. Security concerns related to virtual payment systems and the risk of cyber-attacks persist. As these technologies become more integrated into real estate practices, they force industry leaders to rethink traditional transaction processes and potentially redefine legal frameworks. The next wave of innovation promises to merge digital tools with human touch seamlessly, setting the stage for transformations that redefine the very essence of property buying and selling. But there’s more; what you've learned so far is only the beginning.
The manufacturing sector, long perceived as resistant to rapid change due to its reliance on centuries-old practices, is undergoing a renaissance. Automation technologies are leading the charge, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual labor requirements like never before. Robotics are now seamlessly integrated into assembly lines, performing tasks with pinpoint precision and reliability.
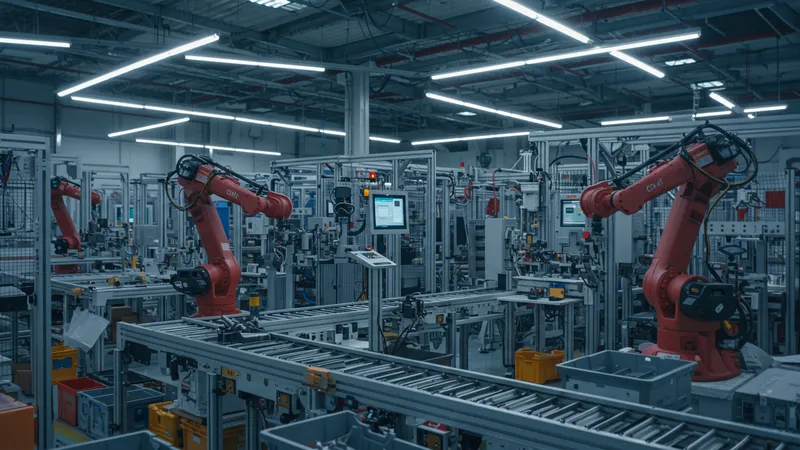
But there's one surprising factor altering the landscape: Collaborative robots, or "cobots," are designed to work alongside humans, enhancing productivity without replacing jobs. This symbiotic relationship optimizes the strengths of humans and machines, fostering an environment where creativity and innovation can flourish alongside technological advancement. More than 2 million cobots are projected to be deployed by 2025, according to industry reports.
Industry giants like Siemens and ABB are providing tools that allow manufacturers to simulate entire production lines digitally before a single piece of machinery is installed. This capability to predict outputs and fine-tune operations ahead of time is a game-changer, potentially saving millions in resources and reducing the time needed to bring products to market.
Yet, the question remains: How do we balance automation with the human element? As automation becomes an increasingly dominant force, retraining and redefining roles for skilled workers will be paramount. Investing in the existing workforce's development could be more significant than ever, ensuring they coexist with—and even drive—these technological advancements. What awaits us in this journey of industrial transformation might redefine our understanding of productivity and human capability forever.
As businesses pivot towards sustainability, manufacturing innovation is no longer about speed and efficiency alone. Today, eco-friendly initiatives are front and center, with companies investing in technologies that minimize environmental impact. From recyclable materials to waste reduction techniques, the manufacturing sector is committed to a green revolution that aligns with global sustainability goals.
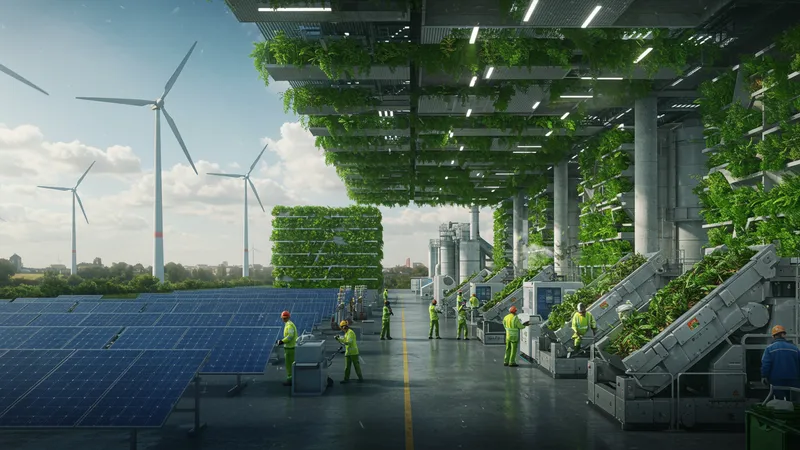

You might find it astonishing that entire factories are powered by renewable energy sources, drastically reducing carbon footprints. The push towards zero-emissions manufacturing is gaining momentum with breakthroughs in energy-efficient machinery and reduction of material waste through advanced recycling processes.
Companies are not just stopping at greening their operations; they're creating end-to-end sustainable value chains. Partnerships are being forged with suppliers and logistics companies that share the same environmental ethos, ensuring that sustainability is not just a marketing gimmick but a fundamental business principle. But there’s one more twist: These shifts in strategy are also elevating corporate reputations, with customer preferences increasingly trending towards brands known for their green initiatives.
The transformation isn't without its challenges, however. The cost and complexity of implementing sustainable practices can be daunting, posing questions about the viability of scaling such initiatives across industries globally. While the journey is complex, the pursuit of sustainability in manufacturing promises not just a cleaner planet but a new brand of innovation inspired by ecological stewardship. We've only scratched the surface of how this commitment to sustainability will redefine industry standards as we know them.
Just as manufacturing is undergoing a sustainable shift, real estate is also embracing eco-friendly practices. The demand for green buildings is skyrocketing as homebuyers increasingly prioritize sustainable living. Environmentally friendly features are becoming standard, from solar panels to energy-efficient appliances. But that’s not the only trend reshaping the sector.
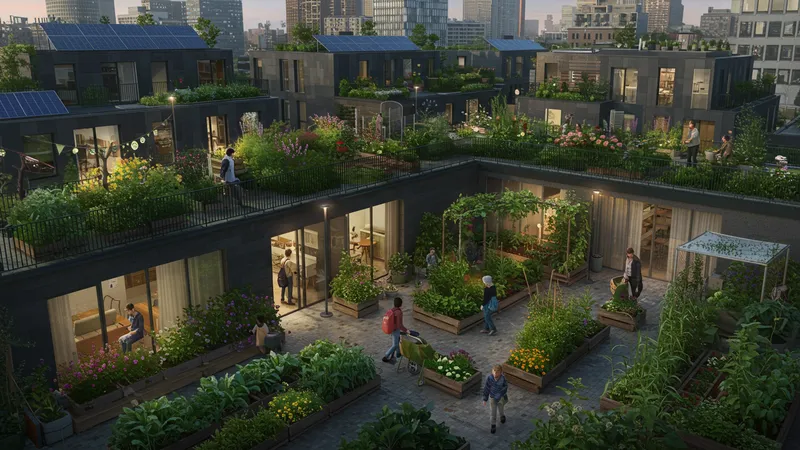

The buzzword in today’s real estate is "net-zero," referring to buildings that produce as much energy as they consume. These structures are designed with advanced insulation techniques, LED lighting systems, and water-saving fixtures to minimize resource usage. Real estate developers are taking things a step further by integrating green spaces—like community gardens and rooftop farms—into urban developments, thus promoting wellness and natural beauty in bustling cityscapes.
However, this green wave brings its own set of challenges. The initial costs for constructing eco-friendly homes can be high, which raises concerns about accessibility for all income levels. Yet, with time, these buildings save significantly on utility costs, offsetting the initial investment. The growing interest in sustainable real estate is driving innovations that aim to bring down these costs, making green living more affordable for the masses.
This transformation signifies a broader trend of environmental consciousness permeating every layer of industry and consumer behavior. What upcoming developments could further tip the scales towards a sustainable future in real estate? The blueprint for the future of living spaces is still being drawn, reserved for visionary designers and tech-savvy builders who dare to imagine an eco-friendly tomorrow.
The integration of technology into real estate goes beyond property viewings and virtual tours. Blockchain technology is making waves by introducing undoable transparency to transactions and ownership records. By digitizing records, blockchain ensures that property transactions are secured and tamper-proof, offering a level of trust that was previously hard to attain.
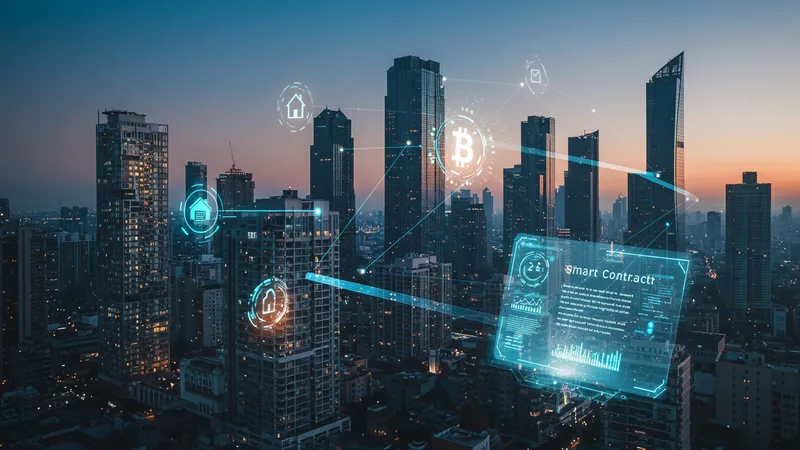

Smart contracts, another byproduct of blockchain, automate and enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries. Imagine a sale going through seamlessly as soon as all conditions are met, verified, and recorded—negating the necessity for a lengthy back-and-forth, which often dampens the buying experience. But this is where the plot thickens: With advantages come challenges in adapting current legal frameworks to embrace these technological innovations.
The combination of AI and big data analytics is further personalizing the home buying experience while empowering real estate professionals with insights never accessible before. Predictive analytics allow agents to anticipate market trends and customer preferences, ensuring they stay a step ahead in a competitive landscape.
Despite rapid technological advancements, the true potential has yet to be realized fully. Can technology help solve long-existing issues like housing affordability and accessibility? The future holds immense possibilities beyond streamlining processes, and the shift towards smarter and more equitable real estate practices might be closer than we think.
The role of robotics in healthcare has been on a steady climb, entering the doors of operating theaters with a quiet but powerful impact. Surgical robots, like those developed by Intuitive Surgical, offer surgical teams precision and control that human hands simply cannot achieve alone. The use of robotics in surgeries not only reduces recovery time but also minimizes the risk of human error.
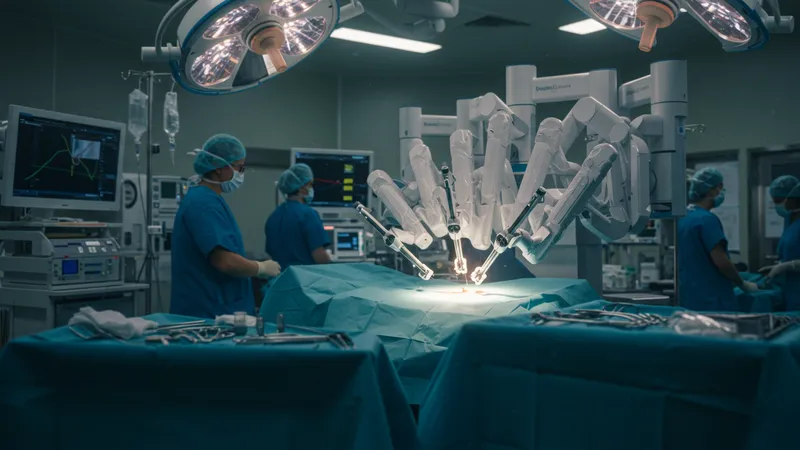
But robotics isn't just about enhancing current procedures; it's about creating possibilities thought unimaginable. For instance, minimally invasive surgeries aided by robotics can be performed with such meticulousness that patient recovery times are slashed by weeks, if not months, altering the entire patient care and recovery landscape. Yet, there’s more: The integration of robotic surgery has raised profound questions about skill and expertise—how do we measure the competence of surgeons who now rely on machines?
These developments push the boundaries of what we perceive as possible in medicine. Imagine remote surgeries being conducted across oceans by specialists using tele-robotic technology. This idea, once a fantastical notion, is now knocking at the doors of reality, striving to bring top-tier medical expertise to underserved regions.
As these applications gain traction, managing innovation alongside tradition poses a challenge. Training for medical professionals needs a revamp to include new technologies, one that balances the art of medicine with the precision of machinery. The implications could reverberate through global healthcare systems, leading us towards an unfamiliar but potentially transformative future for surgery and patient care. What lies ahead may redefine the surgeon's role forever.
The advent of AI in healthcare has not only improved outcomes but has also dramatically reshaped patient experiences. Different from traditional models, AI offers deep insights that enable health professionals to cater personalized care with unprecedented accuracy. AI-driven patient engagement systems remind us to take medications, schedule appointments, and even measure our vitals through connected devices.

Moreover, chatbots and virtual assistants are handling routine inquiries, freeing health professionals to focus on more complex issues, improving the overall efficiency within healthcare systems. But that's just the beginning. Behind the scenes, companies like Babylon Health deploy machine learning to predict health trends on a broad scale by analyzing large datasets, forecasting outbreaks before they begin.
While technology transforms healthcare delivery, ethical dilemmas surface relating to data privacy and security. With personal health information stored digitally, breaches could lead this sensitive data astray. Addressing these concerns is critical for maintaining public trust and ensuring the long-term success of technology in healthcare.
As systems and processes evolve, the promise that AI holds in personalizing patient care poses questions about the future of human elements in healthcare scenarios. How do we preserve empathy and human touch in a digital-first healthcare environment? The efficient delivery of healthcare does not mean the sidelining of human compassion, and the key to the future lies in harmonizing these elements. There’s much more to come as we grapple with these questions.
Artificial intelligence is stepping beyond theoretical application into the very heart of manufacturing processes. AI-powered systems are becoming the brain of factories with advanced predictive maintenance capabilities that flag potential issues before they become costly problems. Companies utilizing these systems report up to a 30% reduction in unplanned downtime, showcasing a striking improvement in operational efficiency.
Production lines previously dependent on human oversight are seeing an infusion of AI, with algorithms determining the most efficient methods to assemble products. By learning and adapting, these smart systems continuously improve the production process. But there’s a twist: As factories become 'smarter', the need for human problem-solving skills increases, requiring staff to adapt and expand their expertise.
Intelligent manufacturing doesn't restrict itself to optimization; it extends to customization, with AI facilitating rapid changes in product designs to cater to market demands. Integration of machine learning allows for the production of bespoke items at mass production costs—a feat previously unimaginable.
Despite these advantages, the challenge remains in adopting AI seamlessly across the entire manufacturing ecosystem. Resistance to change is anticipated from both personnel and infrastructure; thus, future strategies will depend on education and gradual integration to showcase tangible benefits over time. As AI continues to revolutionize the industrial world, businesses must tread wisely to balance the act of innovation and tradition.
As manufacturing evolves, it is poised as a fertile field for investment opportunities. Venture capitalists and corporations alike are pouring funds into innovations that promise to redefine production norms. The trend in smart factories signifies not just a technological shift but also a paradigm shift in attracting a new breed of investment, with tech-centric firms collaborating on unprecedented levels.

Automation, AI, and sustainability form the trifecta that guides modern manufacturing investment strategies. Companies that exemplify these practices see their market valuations skyrocket, providing lucrative investment returns. Crowd-sourced platforms are even giving small-scale investors opportunities to participate in funding the industrial revolution, broadening the scope of funding avenues.
The industrial boom presents governments with avenues to partake by offering incentives for sustainable and innovative manufacturing initiatives. Subsidies, tax breaks, and supportive policies could catalyze innovation by making it financially worthwhile for businesses to invest in updated technologies that promise greener, smarter output.
Nevertheless, challenges accompany these investment opportunities, including volatility in technology trends and adapting to rapid innovation paces. Cultivating a strategic investment mindset focused on long-term value rather than short-term gains will be critical. As the field expands, identifying the most promising developments to back will be the linchpin for success, setting the stage for dynamic shifts in manufacturing investment landscapes.
The rapid industrial transformation is redefining workforce dynamics. The reliance on human labor for repetitive tasks is waning as automation and AI take the forefront, requiring workers to pivot towards roles demanding strategic and innovative thinking. Retraining and upskilling are imperative for industries to sustain their workforce amidst these changes.

The modern manufacturing workforce is not just learning to coexist with technology; it's learning to leverage its strengths. With machinery handling routine operations, human creativity finds new outlets in problem-solving, innovation, and managerial roles. As factories transform, so does the need for cross-disciplinary expertise, merging engineering knowledge with data science and AI proficiency.
However, the shift comes with its challenges. Transition dynamics entail a learning curve and investment in training, which businesses may be wary of. To combat such resistance, initiatives aimed at fostering a culture of continuous learning are crucial, enabling workers to embrace technology's evolving landscape without apprehension.
Interestingly, the industrial shift creates opportunities beyond traditional pathways, allowing a more inclusive workforce. Remote technology lets talent across geographic and demographic boundaries access roles previously out of reach. The redefined roles and pathways chart a course towards a future where technology and human capability flourish side by side, set to transform industries beyond recognition.
The transformation ongoing in healthcare, real estate, and manufacturing is not isolated; they're interconnected, sharing innovations, and driving collective progress. Cross-industry partnerships are enabling the sharing of technology and strategies, promoting a broader application of advancements across sectors.

The interdisciplinary approach fosters innovations that extend beyond a singular industry's capacity. For example, AI tools developed for healthcare now aid in logistics and real estate analytics, optimizing resources across industries from an overarching vantage point.
Also, sustainable initiatives in manufacturing provide frameworks that real estate and healthcare can replicate, promoting eco-friendly practices on larger scales. The cycle of innovation is thus amplified, leading to compounded gains in efficiency, sustainability, and technological prowess.
Although the horizon of cross-industry innovations is promising, the challenges in harmonizing practices and dealing with competitive proprietary technologies remain. Ensuring collaborative unity and breaking silos across different sectors depend on fostering a mindset that prioritizes shared growth and universal advancement. The journey towards comprehensive industry evolution holds potential that could redefine the boundaries and scope of development as we know it.
The web of innovation and disruption in healthcare, real estate, and manufacturing spins a narrative of transformation that's no longer a blueprint of speculation but a reality in motion. From AI's delicate touch in surgery to virtual real estate tours that promise to reshape cityscapes, the confluence of technology and industry presents an era of limitless potential.
Yet for all the promise, the paradigm presents hurdles—not just in adapting to new practices, but also in redefining the ethical contours of our technological future. Keeping our world equitable, safe, and vibrant as technology integrates more deeply into our lives becomes a pressing question.
As for the narratives that build this ever-evolving landscape, the most compelling stories are yet to be written. These stories will determine whether the innovations we're witnessing today mature into societal milestones or tales of unrealized potential. As you absorb these insights, consider your role in shaping the sectors of tomorrow; share, discuss, and delve deeper into the potential that strides ahead, ensuring it becomes a path towards a futurist yet grounded vision.