


Imagine a world where nearly every product you use is crafted with pinpoint precision, all thanks to an unsung hero in the industry: the hydraulic press. This isn't just any tool; it's a game-changer that's revolutionizing modern manufacturing.
As technology evolves at breakneck speed, staying informed about the tools shaping our world is crucial. Hydraulic presses are pushing the boundaries of what's possible, impacting everything from automotive production to medical device creation.
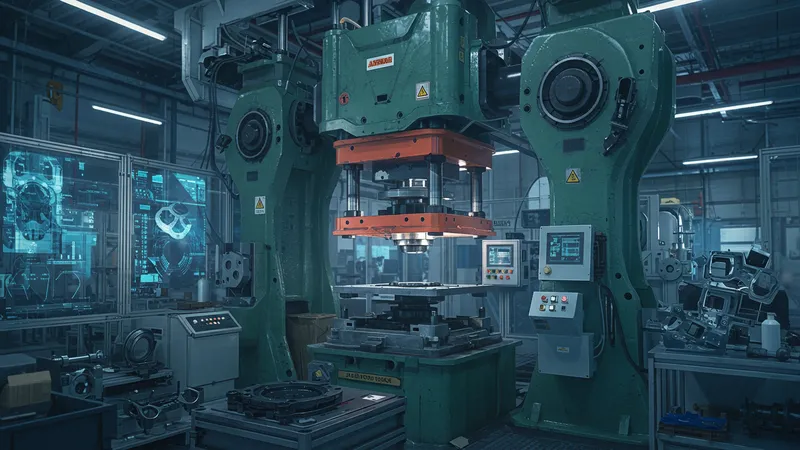
What's astonishing is that many industries still underestimate the potential of hydraulic presses. In sectors dominated by digital technology, these machines operate quietly yet powerfully, performing tasks that require unparalleled force and precision. Many people believe newer technology has left these machines behind, but they couldn't be more wrong. But that’s not even the wildest part…
Consider this: items you never thought possible to manufacture with such finesse are being churned out effortlessly. Even giants like automotive and aerospace industries rely heavily on hydraulic presses to maintain safety and engineering excellence. But the secret lies in the machine's evolution, adapting to needs no one anticipated. What happens next shocked even the experts…
Despite their simplicity, hydraulic presses have evolved to become indispensable in manufacturing. The secret lies in their ability to exert immense pressure, crucial for shaping hard materials. This exceeds the expectations of many engineers. But there’s one more twist…
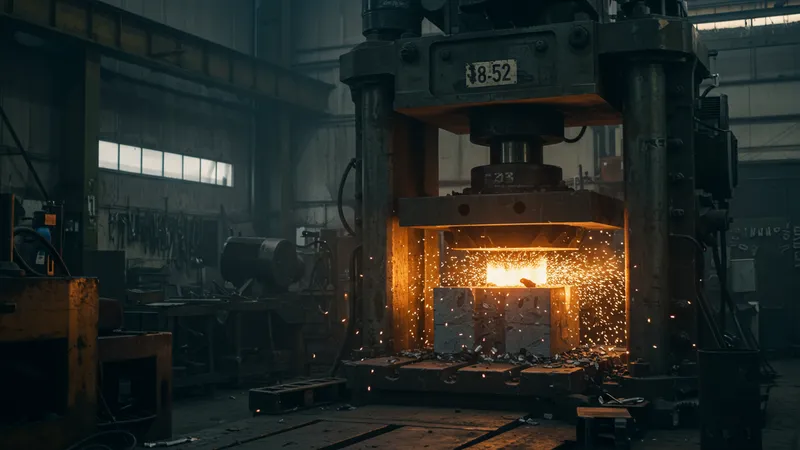
Integration with advanced technology has empowered these machines to handle complex processes efficiently. From computer-controlled systems to custom force sensors, the enhancements are groundbreaking. What you read next might change how you see this forever.
Even as factories implement the latest robotics, the timeless hydraulic press remains resilient. It’s a testament to engineering prowess, maintaining relevance through robust adaptability. But there's more than meets the eye…
The evolution doesn't stop at adaptation. Some suppliers are innovating bi-directional capabilities, allowing unprecedented versatility in production lines. This overlooked development offers a fresh perspective. But wait till you discover what's coming up next…
Peeking behind the factory curtain reveals secrets often missed: industrial machines are a symphony of moving parts with each synchronized movement optimizing production. You might assume this complexity invites chaos, but the opposite is true. But we’ve barely scratched the surface…

Streamlined processes rely on these machines fostering seamless collaboration among production stages. The utilization of such machines is a masterstroke of industry leaders who understand their intrinsic value. Yet, below is another layer that astounds.
Cutting-edge calibration techniques have transformed these machines into more than simple devices. They’re intelligent partners in crafting precise components, capable of incredible feats that rival even the most advanced automated systems. But there's something they don’t tell you about these wonders…
An underlying synergy between human operators and machines is the crux of this manufacturing marvel. Expertise heightens machine potential, unlocking efficiencies that weren’t thought possible. Yet, there's still a lesser-known fact that changes everything…
Alarming rises in environmental concerns have prompted dramatic innovations in machinery. Did you know hydraulic presses are now being engineered to be eco-friendly? The implications are profound, going well beyond mere cost savings. But the narrative doesn’t end here…
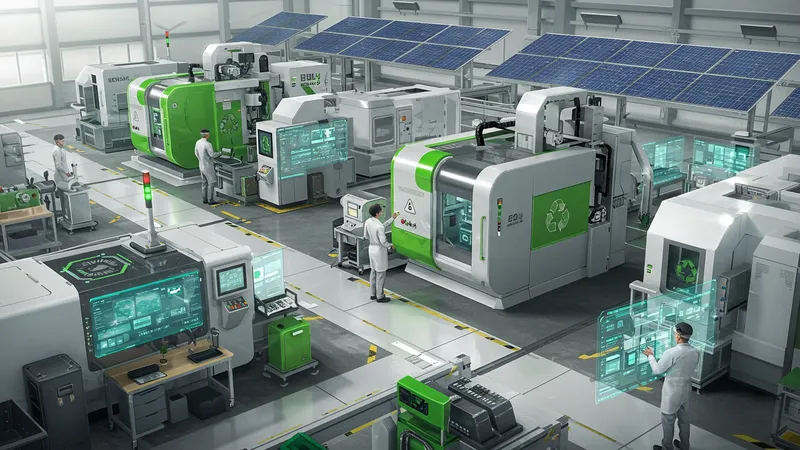
The inclusion of sustainable energy sources in powering these machines marks a significant industry shift. This growing trend isn’t just about going green; it’s a clever strategy to ensure future-proof manufacturing, but it doesn’t stop there.
These advances resonate deeply with eco-conscious suppliers seeking green certifications. The subtle shift to cleaner technologies within these machines is quietly rewriting every rule of production standards. Yet, the full story is even more intriguing.
Maisow, an industry forerunner, leads the charge by integrating renewable energy solutions with hydraulic presses. Their commitment to a cleaner future is setting a new benchmark. What they’ve achieved next is nothing short of revolutionary…
While hydraulic presses offer immense benefits, a deeper dive exposes hidden costs few are aware of. Maintenance, notoriously expensive, can significantly impact a company’s bottom line. But is this the entire truth?

Operational downtime is another costly consideration, frequently overlooked by newcomers eager to invest. The complexities of these machines mean that minor malfunctions could potentially bring production to a halt, which nobody anticipates.
Another unspoken challenge lies in the need for skilled technicians. The value of human expertise is immeasurable, yet often underestimated. Proper maintenance can alleviate some of these hidden costs substantially. But hold on, there’s something else at play…
A lesser-discussed aspect is the need for proper safety measures to prevent risks, overshadowed by output efficiency. These additional investments are crucial to building a sustainable operation. But there’s a surprising twist coming…
Hydraulic presses endure due to their adaptability, especially evident through tech integration. Automation and precision controls have cranked up efficiency tenfold, a remarkable advance in the landscape. But the transformation doesn’t stop there...

The addition of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities offers another dimension. Remote monitoring and maintenance forecasting are now common, dramatically slashing downtime. But, IoT is just one piece of the puzzle that’s shaping your future products…
Advanced software interfaces allow for more intricate and exact specifications. This fine-tuning leads to the production of complex designs that were once deemed impossible. You’ll be astonished at what else awaits your discovery…
There’s also the incredible merging of AI, allowing adaptive behavior in presses to optimize power usage and performance. The synergistic effects vibrate throughout production lines. Yet, one more incredible development is around the corner...
A vibrant future awaits the hydraulic press industry as untapped markets emerge. Industries across the planet are beginning to explore possibilities. But why are they now flocking to this “old” technology?

An unanticipated surge in demand for custom goods finds hydraulic presses at the forefront. This shift signals a ripple effect awakening curiosity in producers worldwide, but there’s much more beneath the surface…
Rapid urbanization in developing regions brings new challenges, but hydraulic press technology offers robust solutions, capable of answering vast infrastructure needs. This is merely the start…
Innovations continue to open doors to sectors previously uninterested. Automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics now see hydraulic presses as strategic assets. The evolution is set to change everything you thought you knew…
Industry veterans often extol hydraulic presses for their reliability, but their advantages run deeper. The capability to apply continuous pressure is significant, transforming how products are made. But there’s more powerful beneath the hood…

From energy conservation to cost efficiency, these machines are a blessing for cost-conscious manufacturers. Their robust design persists through grueling tasks, ensuring long-term operational savings alongside extraordinary power. But other factors await discovery…
Despite initial investments, these presses offer scalability unlike any other. Once incorporated into a production line, they offer unparalleled agility in adapting to new projects without substantial extra costs. This secret weapon has more potential than expected…
At last, their consistent high quality ensures that end products meet stringent industry standards effortlessly—a reputation long envied by counterparts. Hydraulic presses aren’t simply machines; they’re engineering marvels redefining modern manufacturing. But one last surprise remains…
As we explored, the world of hydraulic presses is full of unexpected twists and turns that reshape industries. The revelations go beyond marveling at machines; they forecast a future where creativity meets industrial might. Now, ready to dive deeper? Share, bookmark, or explore further to keep up with the transformative forces shaping manufacturing's future!