

Imagine a world where every light bulb, computer, and factory is at the mercy of the wind. In today's digital age, industrial generators are the silent heroes ensuring that never happens. But what if I told you these marvels could do more than just keep the lights on?
With global power demands skyrocketing, the need for reliable industrial generators is more pressing than ever. These machines are the backbone of modern industry, helping businesses avoid costly downtime and secure their operations against uncertainties. Their impact on our lives is beyond essential.
While you might think of generators as simple backup solutions, recent advancements have turned them into technological powerhouses. Harnessing real-time data analytics, some can diagnose issues before they even happen, drastically reducing maintenance costs. But that’s not even the wildest part…
In certain industries, the choice of a generator can directly affect revenue streams. Companies leveraging the latest generator technology have reported up to a 30% boost in operational efficiency, a business game-changer. But what does this mean for the future of energy? Well, that's where things get really intriguing…
What happens next shocked even the experts—industrial generators are not just preventing blackouts; they're becoming a key player in sustainable energy markets worldwide. These unexpected developments are setting new standards, prompting us to rethink what we know. But how? Keep reading to uncover how these changes might soon impact your city and power bills...
When it comes to industrial generators, not all are created equal. One factor that distinguishes top-tier generators is their fuel efficiency. Advanced designs have minimized waste, optimizing every drop of fuel. These improvements come from ingenious engineering—but there’s one crucial tweak that often gets overlooked...
Did you know some generators can automatically adjust their fuel consumption based on demand? This adaptive technology not only boosts efficiency but slashes operational costs by up to 25%. While this might sound impressive, the real breakthrough lies in its growing influence on renewable energy integration.
Many manufacturers are now adopting hybrid generator systems, which utilize both traditional fuels and renewable sources like wind or solar. This development is paving the way for cleaner, greener power solutions. But there’s one more twist in this story about industrial generators and their evolving role...
Could these innovations mean urban areas no longer suffer from common power outages during peak times? Surprisingly, implementing certain generator technologies has already reduced blackout incidences by a significant margin. But what you read next might change how you see this forever...
At first glance, the price tag on an industrial generator might be intimidating. However, looking at the initial cost alone can be misleading. Consider the long-term savings: reduced downtime, maintenance cost reductions, and energy efficiency. So, what does a complete cost analysis actually reveal?

One surprising truth is that the buy-in cost of advanced generators is quickly offset by their extended lifespan and operational savings. In fact, data shows a return on investment often within three to five years. Here’s the catch, though— picking the wrong generator size can wipe out any potential savings...
An oversized generator means wasted fuel and inflated expenses, whereas an undersized model might struggle to meet energy demands. Strategic sizing and investment in the right model can spell the difference between financial success and disaster. Yet, the story doesn’t end with just getting the size right...
Another lesser-known factor is the impact of purchasing agreement choices. Subscription and leasing options increasingly replace outright purchases, allowing businesses to reap the benefits of the latest technology without the financial commitment. What if I told you there’s more hope for small businesses than ever before?
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, the power grid is undergoing radical changes—and industrial generators are right at the heart of this transformation. They are evolving from mere backup systems into crucial components of distributed energy resources (DERs).
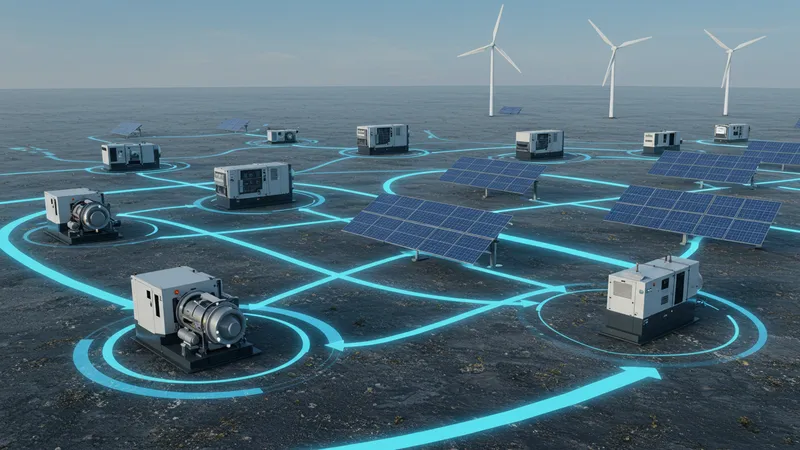

This shift allows generators to feed power back into the grid, especially during high-demand periods, stabilizing supply and reducing strain on traditional electricity sources. But how can this capability further reshape our energy landscape?
With smart grid technology, generators can now communicate with other power resources, enabling a more efficient and reliable energy distribution system. This technological symphony is reshaping expectations from collective power generation tasks, but what happens when the scale tilts?
More homes and businesses are taking advantage of these changes, with microgrids becoming increasingly popular. These localized networks offer independence from central grids, highlighting the empowering shift towards localized and personalized energy solutions. There’s still much more to discover about this ingenious transformation...
As environmental concerns intensify, the demand for eco-friendly power solutions is skyrocketing. Industrial generators, traditionally reliant on fossil fuels, are now being reimagined. Could eco-friendly generators revolutionize not only industries but our approach to environmental stewardship?
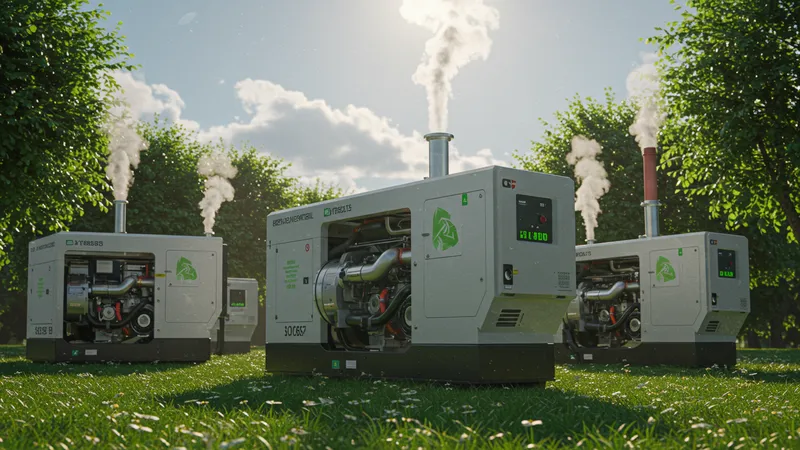

Modern generators utilizing biofuels significantly reduce emissions without compromising power output. Coupled with catalytic converters, these models meet stringent environmental regulations while delivering robust performance. But what’s the catch with these greener alternatives?
Switching to these eco-friendly models requires careful consideration of fuel availability and cost—factors that may influence their adoption speed. Yet, the momentum behind this movement is undeniable, encouraged by incentives for energy sustainability. What’s the hidden incentive pushing even bigger industries to go green?
Governments worldwide are rolling out tax cuts for eco-friendly businesses, making technologies previously considered luxuries more accessible. Such dynamics are reshaping market growth trends and consumer expectations. But there's still much more to explore about the catalytic role of industrial generators...
Natural disasters bring about unexpected power outages, sometimes lasting days or weeks. In such scenarios, industrial generators become indispensable lifelines for communities and industries. But their role goes beyond providing temporary relief; they’re evolving as integral elements in comprehensive disaster preparedness strategies.
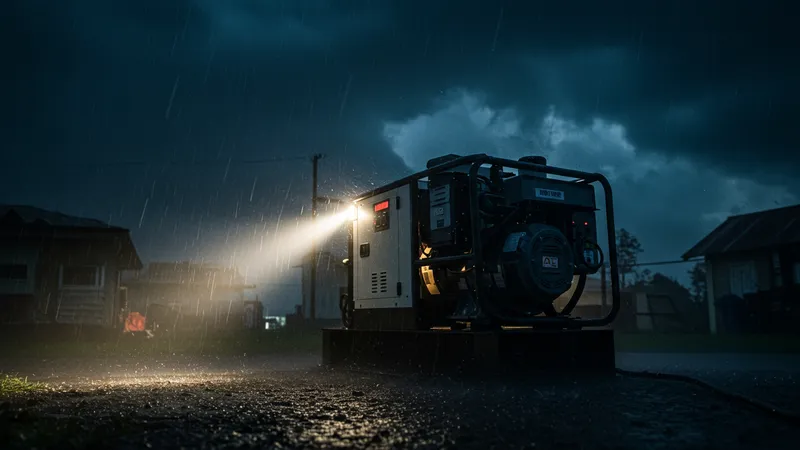

Seamless transition mechanisms from grid to generator power ensure operations aren’t disrupted during crises, maintaining critical services. But what happens when these solutions aren’t enough, and more is needed to keep communities safe?
Certain models come equipped with multi-fuel capabilities, allowing operation despite potential fuel shortages. Meanwhile, the proliferation of portable power solutions is extending reach deeper into affected areas. These advancements are closing critical gaps, yet there’s a surprising element specific to urban disaster strategies...
The integration with smart city frameworks is improving the resilience of metropolitan areas, ensuring that even during blackouts, essential city functions run smoothly. This factor could redefine preparedness levels, leading to a future where society itself becomes more resilient, flexible, and adaptive to crises...
Industries reliant on continuous power—like manufacturing, healthcare, and data centers—cannot afford even momentary disruptions. Here, industrial generators provide peace of mind, eliminating worries of operational halts or data losses. Yet, there are revelations on how these sectors approach power supply enhancement...
The case for dual redundancy in power supply systems is more robust than ever. Generators working alongside UPS systems reduce interruption risks, ensuring seamless operations. Does this redundancy merely add excess, or is the payoff substantial enough to justify the costs?
Interestingly, the upfront investment in redundancy often deters business leaders; however, long-term data highlights consistent savings in downtime-related expenses. Further embedding AI-powered diagnostics into these systems ensures imminent failures are identified early. What’s this technological fusion’s potential in industry transformation?
Predictive maintenance, enabled by smart generators, is rapidly transforming how industries function, paving the way for proactive approaches rather than reactive responses to power solutions. These continuous advances herald a new era of operational stability and global competitiveness...
Selecting the perfect industrial generator involves far more than matching output requirements to specifications. Various factors, from environmental conditions to site-specific needs, play pivotal roles. But how do you navigate this complex landscape to make informed, future-proof decisions?
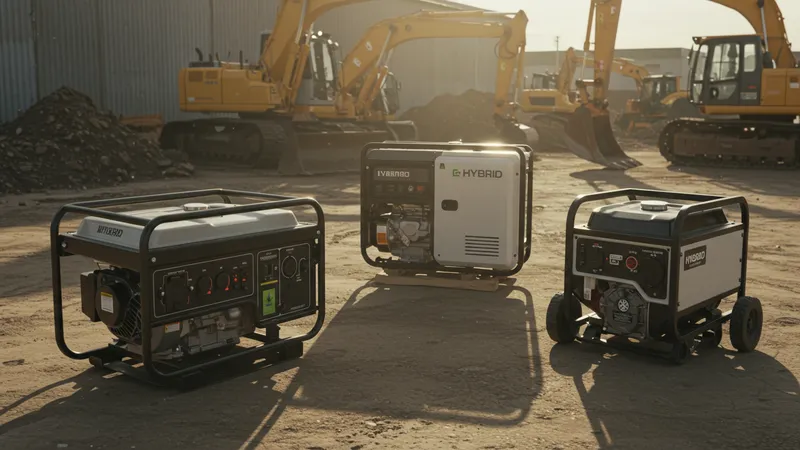

The initial consideration is often the choice between diesel, gas, or hybrid models. Each type has its pros and cons, but the trick lies in understanding your unique operational requirements alongside budget considerations. Is there more to explore beyond these elemental choices?
Another crucial aspect is scalability. Opting for generators that can match growing power demands without replacing existing systems ensures long-term investment efficiency. But it's also about accessory integration, which could unveil further operational enhancements. What potentially overlooked detail could impact your choice significantly?
Considering service and maintenance support from manufacturers guarantees that your systems remain efficient throughout their lifecycle. Many ignore this essential service aspect, embarking on future regrets. With the right foresight and meticulous choice, industrial generators can foster growth and innovation in any enterprise...
Industrial generators continue to undergo revolutionizing changes far beyond basic functionality improvements. Recent developments have birthed game-changing innovations that could significantly alter industrial practices. Just what are these advancements that everyone in the industry is talking about?
The rise of digital twins is one such innovation—virtual representations of generators allowing for unprecedented simulation, monitoring, and analysis. This advanced tool offers manufacturers insights into operations without physical machine borders. But could these technological shifts redefine real-world applications?
Enhanced Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity empowers generators to interact with broader infrastructural systems drastically influencing reliability and performance metrics. The impact? Enhanced connectivity may well revolutionize urban development zones—but the expansive benefits don't stop there...
The integration of blockchain into operational data transfer ensures secure and transparent energy management, further boosting reliability and accountability. Such innovative leaps forward are changing the industrial landscape, highlighting the immense potential of modern generators...
Aspiring for energy independence is no longer a far-fetched concept—industrial generators are bridging this ambition with reality. Recognizing these innovations' potential could empower shifts toward a more autonomous energy future. But precisely how would this master plan unfold?
Localized microgrid developments buttressed by advanced generator technologies create islands of independence, reducing dependency on larger, often unreliable grids. This progressive movement foreshadows a more resilient energy ecosystem, but what does this mean for large-scale industrial reliance?
The democratization of energy resources allows for broader access and control over power generation means, dismantling centralized monopolies. Interestingly, it's not just about breaking free from existing power constraints—could this revolution have broader geopolitical ramifications?
Countries now recognize their energy security correlates directly to industrial advancement. As more regions adopt these solutions, a trend toward self-reliance could stabilize economies previously susceptible to energy fluctuations, ushering in a transformative era of power distribution...
Despite their forward momentum, the industrial generator market faces several hurdles that could hamper future growth. As demand rises globally, manufacturers encounter critical challenges affecting production, development, and innovation evolution. What’s obstructing this multi-billion dollar industry’s path to success?

The supply chain complexities pose significant threats due to raw material scarcity impacting production consistency. Meanwhile, the Covid-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global logistics systems, escalating these issues further. But could these obstacles precipitate operational pivots within the industry?
With climate-related regulations spearheading greener initiatives, the challenge arises for manufacturers to align with sustainability goals without jeopardizing cost-effectiveness. Fusing economic considerations with ecological impacts drives the industry towards a transformative yet complex crossroads. What unexpected variables could emerge from these environmentally-driven changes?
Innovation's fast pace presents its highs and lows, with smaller firms struggling to maintain competitive ground beside industry giants. Despite challenges, overcoming these constraints unlocks boundless potential for the global generator market—with each hurdle presenting a disguised opportunity for advancement...
In volatile times, backup power systems serve as crucial lifelines. With emergency preparedness evolving, industrial generators ensure continuity amid disasters or infrastructure failures. Their role has adaptively expanded, demanding nuanced, rapid deployment strategies. Just how has this field revolutionized?
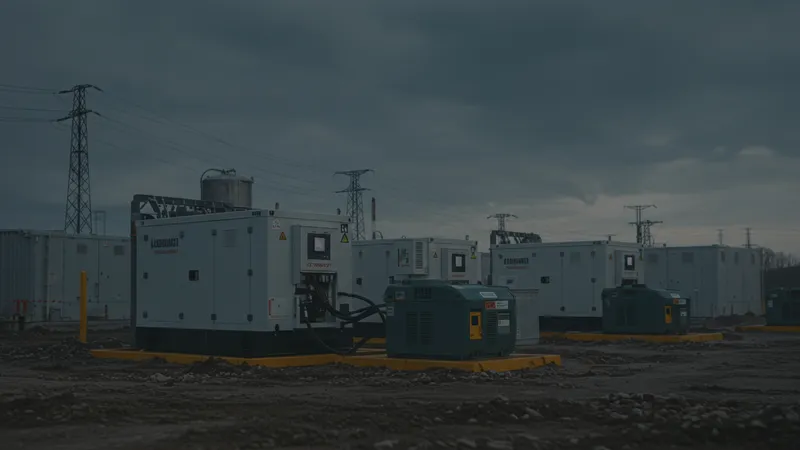

Today's emergency power systems incorporate modular, portable units capable of rapid deployment in critical scenarios. Such systems lend flexibility within diverse operating environments, addressing immediate hurdles with minimal logistical interference. But does this shift enhance permanent infrastructure functionalities?
Hybrid technology finds its footing in this domain—integrating renewable energy sources alongside traditional fuels provides uninterrupted service even when primary systems falter. But can this hybrid composition extend beyond temporary solutions to ultimately regularize usage across broader applications?
Continual enhancement ensures greater readiness, minimizing resource strain during high-pressure situations. As emergency response becomes more sophisticated, expect core processes to evolve, ultimately simplifying task execution while reinforcing reliability... as society moves through unexpected trials toward assured stability...
Many remote areas face glaring energy deficits, creating exceptional vies for industrial generators. Renewable energy renderings form potential pathways toward sustainable, enduring solutions. Emerging technological leaps literalized generator inclusivity on a massive scale—what do these advances herald for isolated communities?
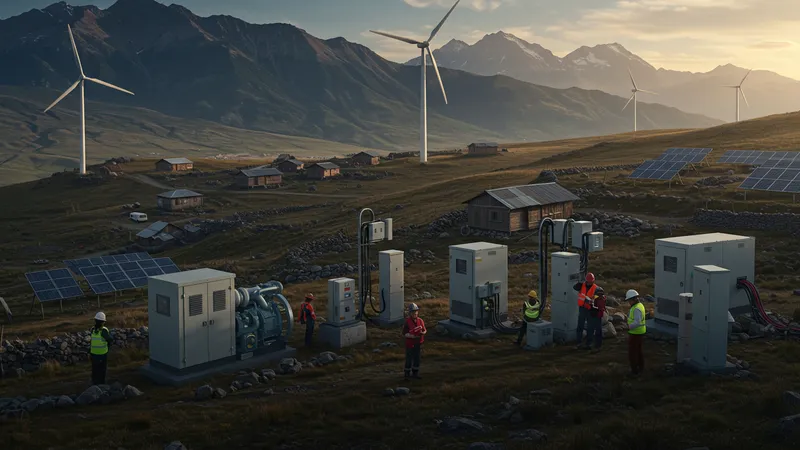

Enhanced hybrid technology availability augments energy inclusivity within remote locales. Flexible, adaptive systems prompt self-sufficiency while diminishing utility dependency. Could this movement symbolize localized autonomy, or will distance continue dictating cost constraints on remote access solutions?
Integrating solar, wind, and biofuel generators overhauls remote grid infrastructure, significantly cutting maintenance while promoting internal self-sustenance. Thriving under adverse conditions unveils newfound sustainability lanes for sequestered localities. Just how might further decentralized development reshape broader communities?
Investment incentives for off-grid solutions spur long-term collaboration between governments, corporations, and stakeholders. Beyond bridging societal energy gulfs, the deeper perennial benefits lie in escalating economic development potential for previously neglected regions...
The future of power generation is a thrilling ride, driven by technological leaps we see in industrial generators. This fast-changing landscape holds lessons for businesses, governments, and individuals: adaptability is king. As we advance, the takeaways are clear: foreseeing and investing in these shifts aren't just strategic; they're imperative for future-readiness.

Now more than ever, understanding and embracing these innovations isn't optional—it's the key to thriving in tomorrow's economy. Share this article, bookmark it, and become a part of the movement toward smarter, greener energy solutions. Let's future-proof our world one generator at a time!